A peanut is not a nut, but actually a seed. In addition to containing protein, a peanut is rich in fats and carbohydrates. Fats and carbohydrates are the major sources of energy for plants and animals.
The energy contained in the peanut actually came from the sun. Green plants absorb solar energy and use it in photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide and water are combined to make glucose. Glucose is a simple sugar that is a type of carbohydrate. Oxygen gas is also made during photosynthesis.
The glucose made during photosynthesis is used by plants to make other important chemical substances needed for living and growing. Some of the chemical substances made from glucose include fats, carbohydrates (such as various sugars, starch, and cellulose), and proteins.
Photosynthesis is the way in which green plants make their food, and ultimately, all the food available on earth. All animals and nongreen plants (such as fungi and bacteria) depend on the stored energy of green plants to live. Photosynthesis is the most important way animals obtain energy from the sun.
Oil squeezed from nuts and seeds is a potential source of fuel. In some parts of the world, oil squeezed from seeds-particularly sunflower seeds-is burned as a motor fuel in some farm equipment. In the United States, some people have modified diesel cars and trucks to run on vegetable oils.
Fuels from vegetable oils are particularly attractive because, unlike fossil fuels, these fuels are renewable. They come from plants that can be grown in a reasonable amount of time.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
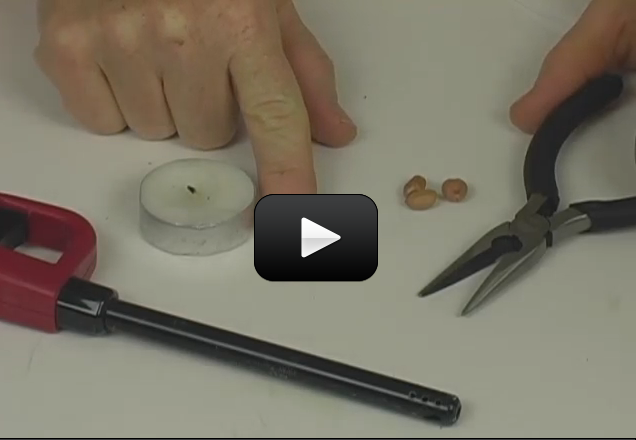



 The atoms in a solid, as we mentioned before, are usually held close to one another and tightly together. Imagine a bunch of folks all stuck to one another with glue. Each person can wiggle and jiggle but they can’t really move anywhere.
The atoms in a solid, as we mentioned before, are usually held close to one another and tightly together. Imagine a bunch of folks all stuck to one another with glue. Each person can wiggle and jiggle but they can’t really move anywhere.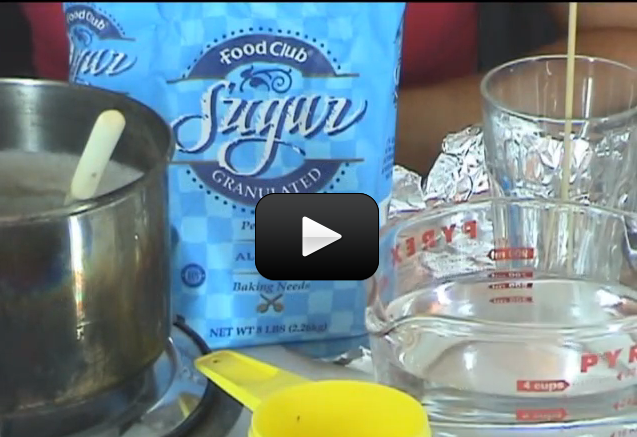
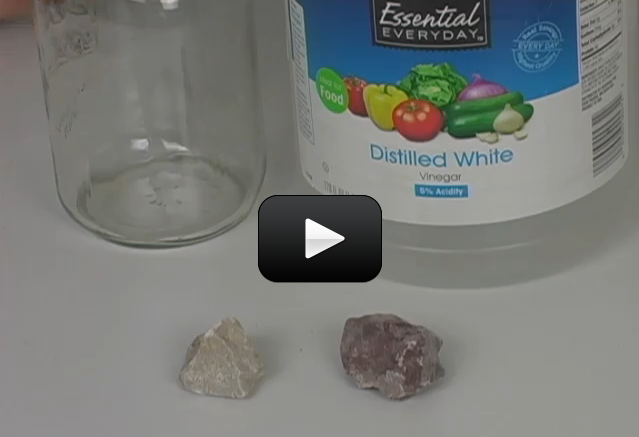
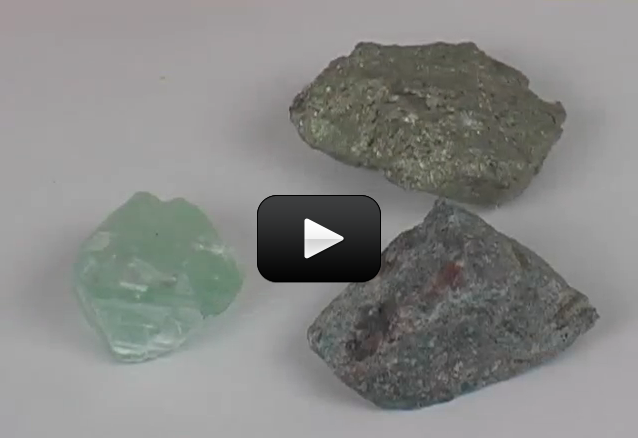
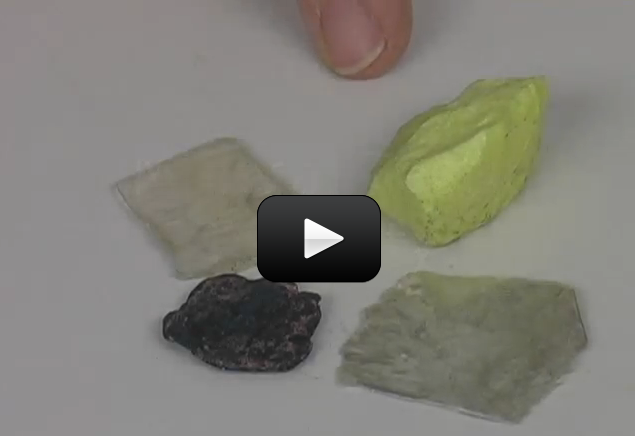
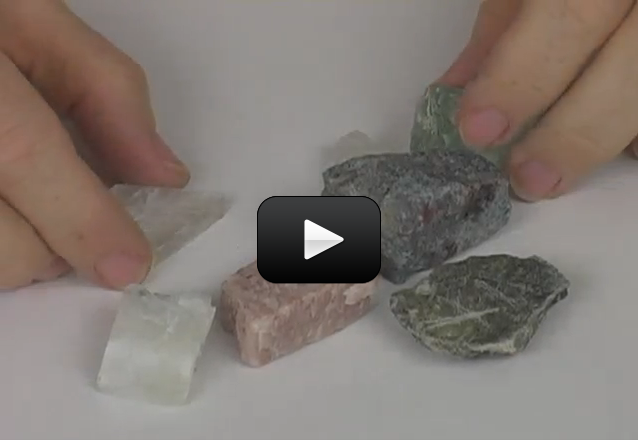







 If you’ve ever eaten fruits or vegetables (and let’s hope you have), you have benefited from plants as food. Of course, the plants we eat have been highly modified by growers to produce larger and sweeter fruit, or heartier vegetables.
If you’ve ever eaten fruits or vegetables (and let’s hope you have), you have benefited from plants as food. Of course, the plants we eat have been highly modified by growers to produce larger and sweeter fruit, or heartier vegetables.


 Broccoli, like all plants, has chlorophyll, making it green. You can really “see” the chlorophyll when you boil broccoli. This is such a simple experiment that you can do this as you prepare dinner tonight with your kids. Make sure you have an extra head of broccoli for this experiment, unless you really like to eat overcooked broccoli.
Broccoli, like all plants, has chlorophyll, making it green. You can really “see” the chlorophyll when you boil broccoli. This is such a simple experiment that you can do this as you prepare dinner tonight with your kids. Make sure you have an extra head of broccoli for this experiment, unless you really like to eat overcooked broccoli.


 Grab a handful of buttons. Make sure there are all different kinds and colors.
Grab a handful of buttons. Make sure there are all different kinds and colors.
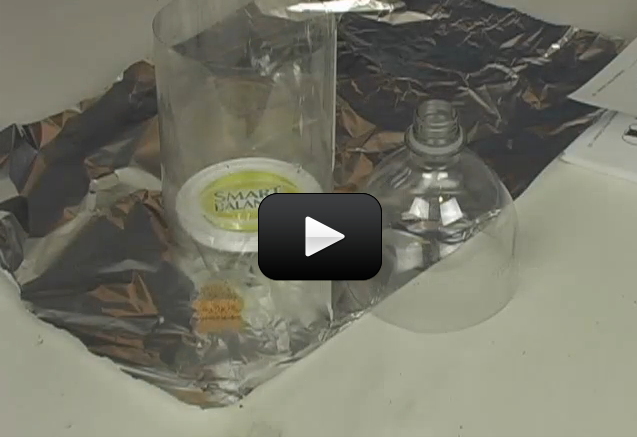
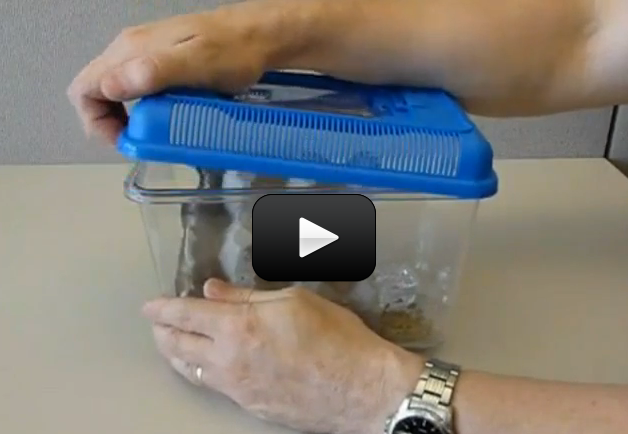
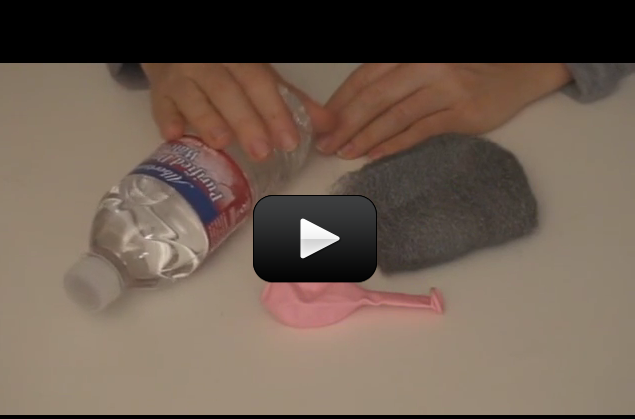
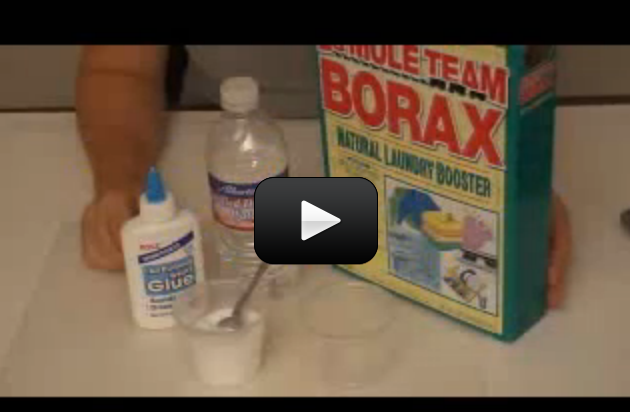
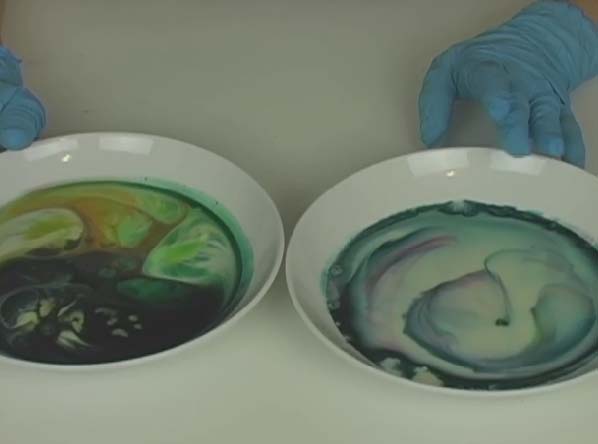
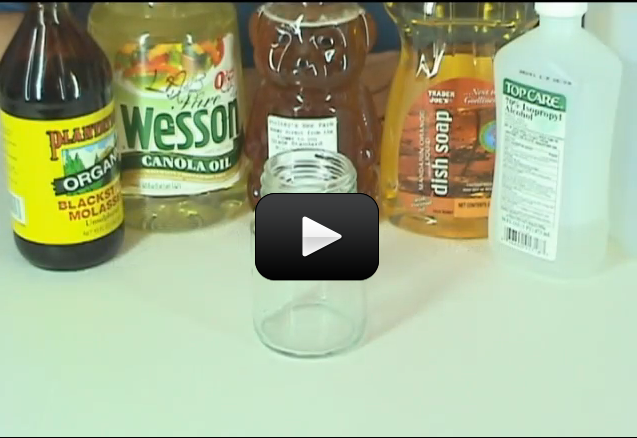
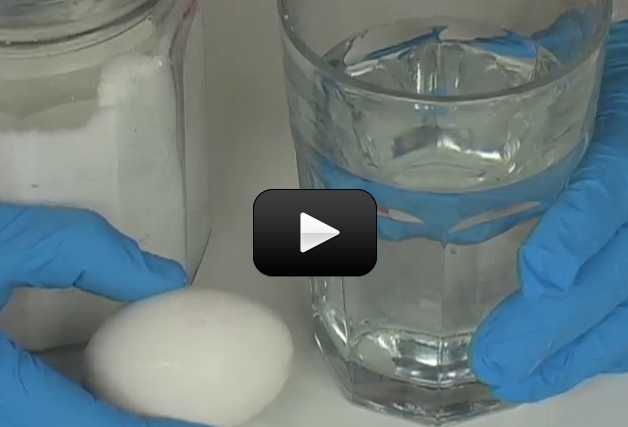





















 When you warm up leftovers, have you ever wondered why the microwave heats the food and not the plate? (Well, some plates, anyway.) It has to do with the way microwaves work.
When you warm up leftovers, have you ever wondered why the microwave heats the food and not the plate? (Well, some plates, anyway.) It has to do with the way microwaves work.
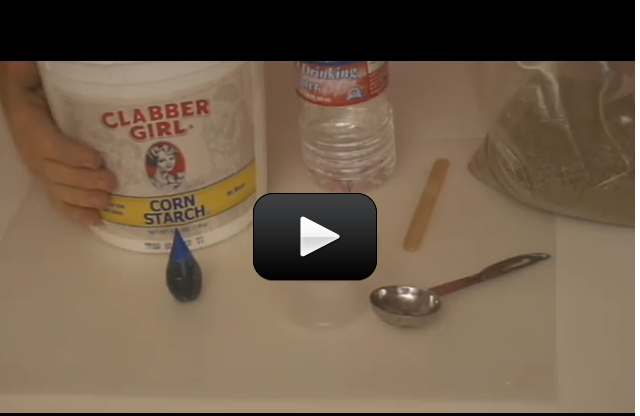


 Can we really make crystals out of soap? You bet! These crystals grow really fast, provided your solution is properly saturated. In only 12 hours, you should have sizable crystals sprouting up.
Can we really make crystals out of soap? You bet! These crystals grow really fast, provided your solution is properly saturated. In only 12 hours, you should have sizable crystals sprouting up.

 Did you know you can create a compound microscope and a refractor telescope using the same materials? It’s all in how you use them to bend the light. These two experiments cover the fundamental basics of how two double-convex lenses can be used to make objects appear larger when right up close or farther away.
Did you know you can create a compound microscope and a refractor telescope using the same materials? It’s all in how you use them to bend the light. These two experiments cover the fundamental basics of how two double-convex lenses can be used to make objects appear larger when right up close or farther away.
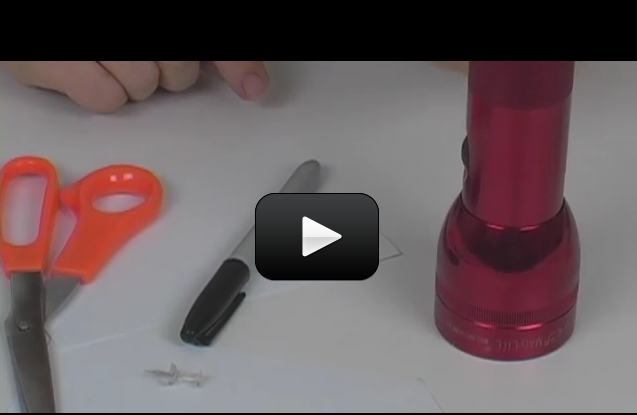




 It just so happens that the Sun’s diameter is about 400 times larger than the Moon, but the Moon is 400 times closer than the Sun. This makes the Sun and Moon appear to be about the same size in the sky as viewed from Earth. This is also why the eclipse thing is such a big deal for our planet. You’re about to make your own eclipses as you learn about syzygy.
It just so happens that the Sun’s diameter is about 400 times larger than the Moon, but the Moon is 400 times closer than the Sun. This makes the Sun and Moon appear to be about the same size in the sky as viewed from Earth. This is also why the eclipse thing is such a big deal for our planet. You’re about to make your own eclipses as you learn about syzygy.






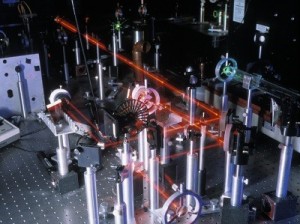 An optical table gives you a solid surface to work on and nails down your parts so they don’t move. This is an image taken with Schlieren photography. This technique picks up the changes in air density (which is a measure of pressure and volume).
An optical table gives you a solid surface to work on and nails down your parts so they don’t move. This is an image taken with Schlieren photography. This technique picks up the changes in air density (which is a measure of pressure and volume).














 Imagine you’re a painter. What three colors do you need to make up any color in the universe? (You should be thinking: red, yellow, and blue… and yes, you are right if you’re thinking that the real primary colors are cyan, magenta, and yellow, but some folks still prefer to think of the primary colors as red-yellow-blue… either way, it’s really not important to this experiment which primary set you choose.)
Imagine you’re a painter. What three colors do you need to make up any color in the universe? (You should be thinking: red, yellow, and blue… and yes, you are right if you’re thinking that the real primary colors are cyan, magenta, and yellow, but some folks still prefer to think of the primary colors as red-yellow-blue… either way, it’s really not important to this experiment which primary set you choose.)
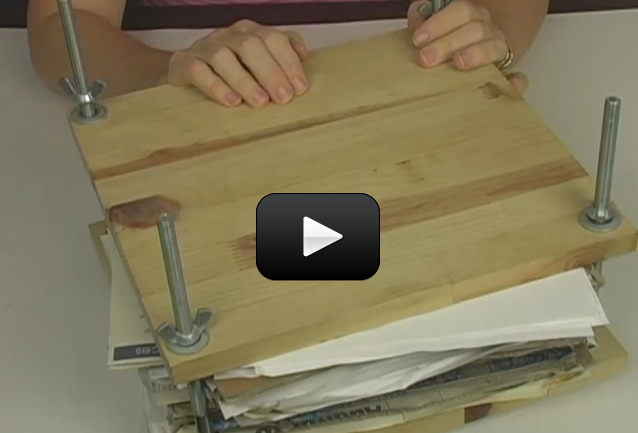
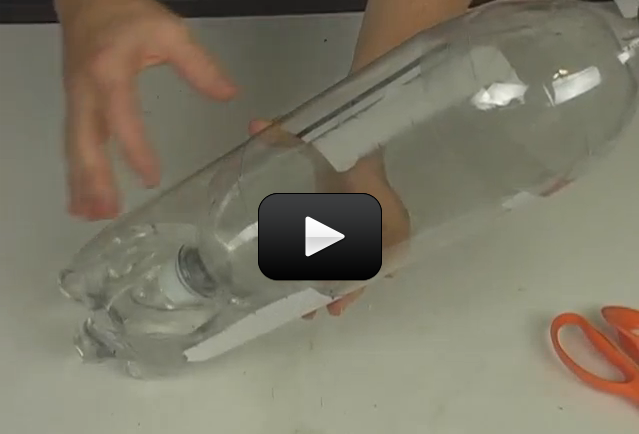




 Flowering plants can be divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons (monocots and dicots). The name is based on how many leaves sprout from the seed, but there are other ways to tell them apart. For monocots, these will be in multiples of three (wheat is an example of a monocot). If you count the number of petals on the flower, it would have either three, six, nine, or a multiple of three. For dicots, the parts will be in multiples of four or five, so a dicot flower might have four petals, five petals, eight, ten, etc.
Flowering plants can be divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons (monocots and dicots). The name is based on how many leaves sprout from the seed, but there are other ways to tell them apart. For monocots, these will be in multiples of three (wheat is an example of a monocot). If you count the number of petals on the flower, it would have either three, six, nine, or a multiple of three. For dicots, the parts will be in multiples of four or five, so a dicot flower might have four petals, five petals, eight, ten, etc.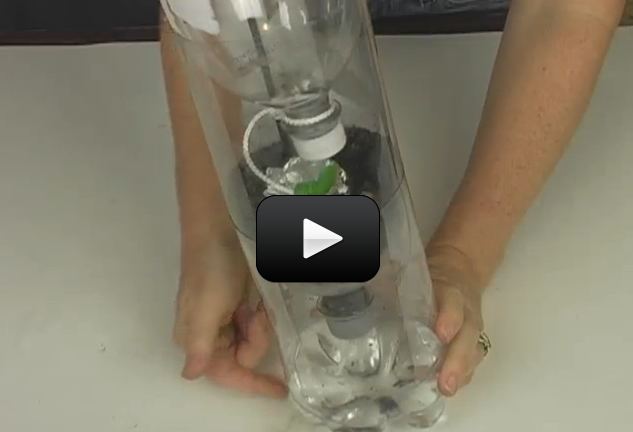
 When birds and animals drink from lakes, rivers, and ponds, how pure it is? Are they really getting the water they need, or are they getting something else with the water?
When birds and animals drink from lakes, rivers, and ponds, how pure it is? Are they really getting the water they need, or are they getting something else with the water?


 Sound can change according to the speed at which it travels. Another word for sound speed is pitch. When the sound speed slows, the pitch lowers. With clarinet reeds, it’s high. Guitar strings can do both, as they are adjustable. If you look carefully, you can actually see the low pitch strings vibrate back and forth, but the high pitch strings move so quickly it’s hard to see. But you can detect the effects of both with your ears.
Sound can change according to the speed at which it travels. Another word for sound speed is pitch. When the sound speed slows, the pitch lowers. With clarinet reeds, it’s high. Guitar strings can do both, as they are adjustable. If you look carefully, you can actually see the low pitch strings vibrate back and forth, but the high pitch strings move so quickly it’s hard to see. But you can detect the effects of both with your ears.
 Sound is everywhere. It can travel through solids, liquids, and gases, but it does so at different speeds. It can rustle through trees at 770 MPH (miles per hour), echo through the ocean at 3,270 MPH, and resonate through solid rock at 8,600 MPH.
Sound is everywhere. It can travel through solids, liquids, and gases, but it does so at different speeds. It can rustle through trees at 770 MPH (miles per hour), echo through the ocean at 3,270 MPH, and resonate through solid rock at 8,600 MPH.
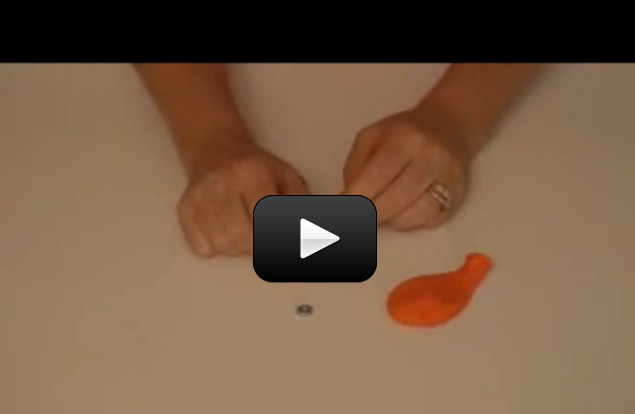

 This is the experiment that all kids know about… if you haven’t done this one already, put it on your list of fun things to do. (See the tips & tricks at the bottom for further ideas!)
This is the experiment that all kids know about… if you haven’t done this one already, put it on your list of fun things to do. (See the tips & tricks at the bottom for further ideas!)